In this article, let’s learn about creating your own command in Linux. Yes, it’s about creating an alias command.
Before we begin, I wish to narrate how the idea of writing this blog started.
One of the followers of my blog asked me,
“Hey Arun! I wonder about your brain’s capability to store a lot of commands. How is that possible?”.
“I’ve been learning Linux and writing code since I joined college (almost 7+ years). During that time I encountered a lot of errors and solved each and everyone on my own which helped me to master it. “, I replied.
“Even then, how could you memorize those flags and options along with each command”, he enquired.
“I cannot memorize each and every command with its options and flags. So, I create my own commands.”, I replied.
“What? You created your own command. Can I create my own command?”, he asked with at most excitement.
“Yes. You can. It’s called alias command in Linux”, I replied.
He asked me to write a blog on it and here it is. Let’s learn about alias command in this blog.
Alias commands in Linux
The alias command provides a string value that shall replace a command name when it is encountered. The alias command lets you create shortcuts for long commands, making them easier to remember and use. It will have the same functionality as if the whole command is run.
How to create your own command?
Using alias command, you’ll be able to create your own command. It’s so simple to create your own command.
Here’s the syntax for the alias command,
Let’s look at an example of creating your own command.
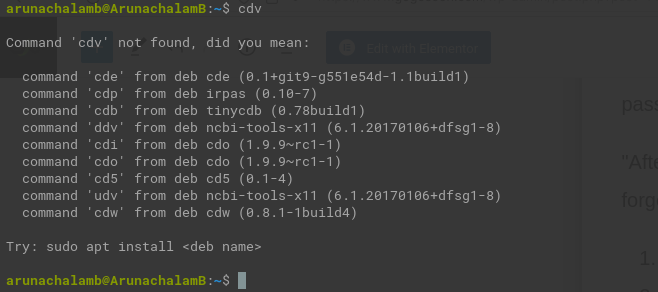
Let’s assume you want to create a command called cdv, and entering the command on the terminal, should take you to the Videos directory.
Usually, to navigate to a directory, we use cd command. To navigate to Videos we need to use cd Videos as shown in the below screenshot.

Videos directoryLet’s create our command cdv to navigate to the Videos directory. To achieve that, you have to enter the following command in your terminal.

alias) command to create our own commandWe have created our command. From the above screenshot, you can see that it does not return anything.
But, How can we verify that the command is created and it is working?
There’s only one way to verify if the command is working. That’s by executing the created command.
Run the cdv command on your terminal.

cdv commandBOOM!!! You created your command.
How to view created alias commands
You may get the following question.
Let’s assume I created multiple alias commands. How can I view all of them together? How can I view the equivalent command of my alias?
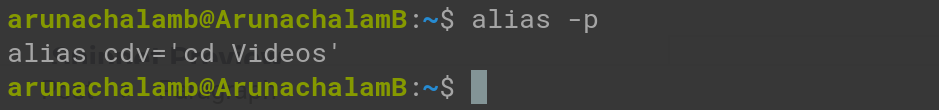
You can view all your alias commands by append -p flag with alias command.
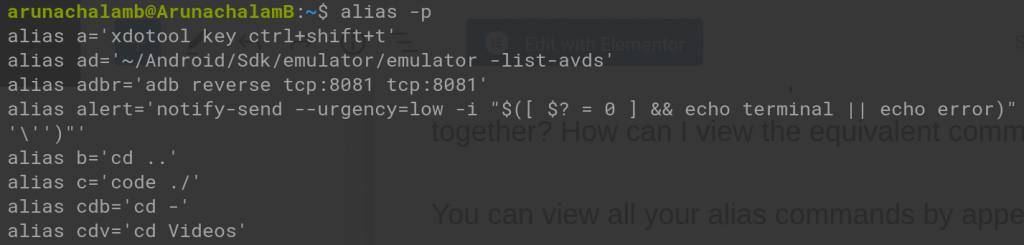
I have created many alias commands. From the above screenshot, you can see all the alias commands that I’ve created.
How to remove an alias command
Pass your alias name to the unalias command as an argument to remove the alias command.
How to remove all alias commands
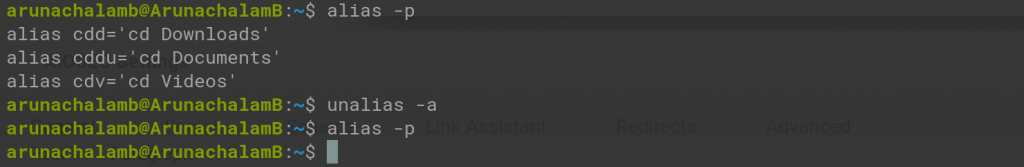
Let’s assume you have added around 20 alias commands. After some time, you realized that using alias commands will make you forget other commands in the long term. Fearing that you wish to remove all the alias commands.
We have a command to achieve that. That is,
I hope you may be curious to know one thing that I’ve written in the above passage.
“After some time, you realized that using alias commands will make you forget other commands in the long term”
- Will someone ever get this feeling?
- Is it true?
The answer to your first question is, Yes. Definitely, you’ll get this feeling when you’re learning and trying out alias commands. Because I had the same feeling.
The answer to your second question is, Absolutely No. This will result in increased productivity. There’s a high chance that you’ll forget the command you created but you’ll never forget the original command. Hence I’ll always recommend revisiting your alias commands often and ensure you’re using all the alias commands you created.
I have a shocking surprise for you. Open a terminal window, create an alias command (cdv). Open another terminal window and type cdv command there.
Surprised?
Yes. If you create an alias command, it’ll be active only for the particular instance of the terminal. It’ll not be created permanently and so, you’ll not be able to access it in two different terminal windows unless you run the alias command on both terminals.
How to create a permanent alias command
To create a permanent alias command, you have to add the alias command to the shell configuration file. There are many shell configurations available. A few of the well-known shells are,
- Bash – ~/.bashrc
- Zsh – ~/.zshrc
- Fish – ~/.config/fish/config.fish
Most Linux distros work with bash, so let’s look at creating a permanent alias in the bash shell. Other shells work pretty much the same.
Let’s open the .bashrc file using vim.
Navigate to the bottom of the file and press i to enter the Insert mode. Add the alias command you want to add permanently.
Save and exit vim by pressing Esc key and typing :wq.
Every time you make a change to the shell configuration file, you have to reload the file again for your changes to take effect immediately.
All the terminal windows you open from now will contain your alias command by default.
alias commandsYou may open multiple windows and check by entering the alias -p command.
Bonus Tip
Here’s a bonus for you all.
We, at GoGoSoon, follow common alias commands, which we set up in everyone’s machine on onboarding. If people wish to add their command, they’ll be able to add on their own and it’ll not be reflected in others (built with the OCP principle in thought). We feel highly productive in using those commands.
I’ve planned to share a part of those commands with you all.
You can either follow the instructions in the README file of this repo or follow the instructions below to set up the alias commands on your machine.
Navigate to the Home folder
Clone the repo
Clone the alias commands repo from GitHub
Add a reference to the alias command file
Open the ~/.bashrc file using vim
Add the following line at the end of the file
Save and exit vim by pressing Esc and typing :wq
Reload the terminal
Reload the terminal by running the following command
That’s it. You’re all set. To verify if the setup is done and it’s up and running, run the following command in the terminal.
You’ll be asked to enter your name. Type your name and press Enter,
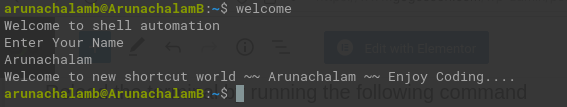
You’ve installed it the right way if you get the above message.
Let me explain the alias commands you’ll have access to using this repo.
| Alias Command | Original Command | Description |
| f | cd $1 | Go forward. Navigate to the next specified directory |
| b | cd .. | Go backward. Navigate back 1 directory |
| c | code ./ | Open Visual Studio Code in the current directory |
| e | exit | Close the terminal tab/window |
| home | cd ~ | Navigate to the home directory |
| a | xdotool key ctrl+shift+t | Open a new terminal tab |
| cdb | cd - | Go to the last directory where you were previously |
| gst | git status | Find the status of the git repo |
| gpr | git pull -r | Pull and rebase the git commits |
| glovim_a_quick_getting_started_guideglo | git log --oneline | Show git commit logs in a single simplified line |
| gcl | git config -l | Show the git configuration of the current repo |
| gca | git commit --amend | Add the current changes to the existing commit |
| gcane | git commit --amend --no-edit | Add the current changes to the existing commit without editing the existing commit message |
| ad | ~/Android/Sdk/emulator/emulator -list-avds | Show available android emulators |
| off | | Turn off your machine |
| bb | | It’s an advanced version of go back command. Entering the b command goes back to only one directory. But entering bb goes back to 2 directories. If you want to go 5 directories back, run bb 5 command |
| vim_a_quick_getting_started_guidepokill | kill $(lsof -t -i:$1) | Kill the program running on the port |
| cc | sudo nano ~/x-commands/aliasCommands.sh | Edit the alias commands file |
| bc | sudo nano ~/.bashrc | Edit the .bashrc file |
| scc | source ~/x-commands/aliasCommands.sh | Refresh the terminal after updating an alias command |
| bcc | source ~/.bashrc | Refresh the terminal after updating .bashrc file |
| welcome | | Verify if alias commands installation is done right |
If you look at the aliasCommands.sh file carefully, I would have added a few functions. You may wonder why I use functions. Read more to have a quick dive into this topic.
How to run multiple commands in a single alias command
You can achieve this in 2 ways. Let me explain both of them here.
Let’s learn this with an example.
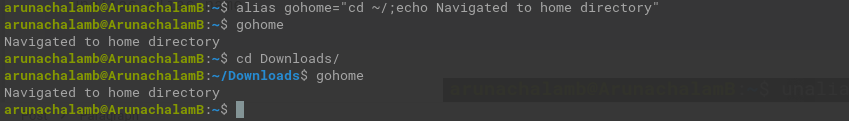
You have to create an alias command called gohome. Running this command, should take you to the home directory and display the “Navigated to home directory” message.
Way 1
This way is the usual way of adding a alias command. You have to add the two commands separated by a semicolon(;).
Way 2
This is a bit different way. To achieve this you have to make a change in your .bashrc file. You have to define a function in .bashrc file with all the commands nested within that.
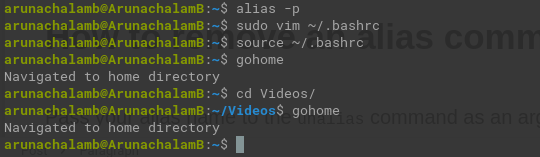
Open the .bashrc file using vim.
Enter INSERT mode by pressing i key.
Create a function named gohome with the above 2 commands.
Save and exit vim by pressing Esc key and typing :wq on command mode.
Reload the terminal by running source ~/.bashrc and you’ll be able to verify gohome command now.
Note:
Creating a function will not list it as an alias command on running alias -p command.
Conclusion
In this article, you have learnt about creating your own (alias) command in Linux. Using an alias command will definitely increase your productivity. I’ve witnessed exponential growth in many people after seeing them using alias commands. I would recommend you all setup your own alias commands.
To learn more about Linux, subscribe to my article by entering your email address in the below box.
Have a look at my site which has a consolidated list of all my blogs.